Discovering unexpected bumps in the vaginal area can be a source of concern, but understanding their causes and knowing how to treat vaginal bumps effectively can bring immense relief and reassurance. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the common culprits behind these unwelcome guests and provide actionable steps for managing them, empowering you with knowledge and confidence.
Understanding the Landscape: What Are Vaginal Bumps?
Vaginal bumps, often referred to as vulvar bumps or labial bumps, are a common occurrence and can manifest in various forms. They can range from small, flesh-colored protrusions to red, inflamed lesions, and their presence can be accompanied by itching, pain, or discharge. It’s crucial to remember that not all vaginal bumps are cause for alarm, and many are benign and easily treatable. However, understanding the potential origins is the first step towards effective management and how to treat vaginal bumps with informed care.
Common Culprits Behind Vaginal Bumps: A Closer Look
To effectively address how to treat vaginal bumps, we first need to identify what might be causing them. The vaginal and vulvar regions are delicate ecosystems, susceptible to a variety of factors.
H3: Infections: The Usual Suspects
Infections are among the most frequent reasons for vaginal bumps. These can be bacterial, viral, or fungal in nature.
H4: Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
While BV doesn’t typically present as distinct bumps, it can cause irritation and inflammation that might lead to small, red bumps or a general feeling of rawness. BV is an imbalance of the naturally occurring bacteria in the vagina. Symptoms often include a thin, grayish discharge with a fishy odor, itching, and burning.
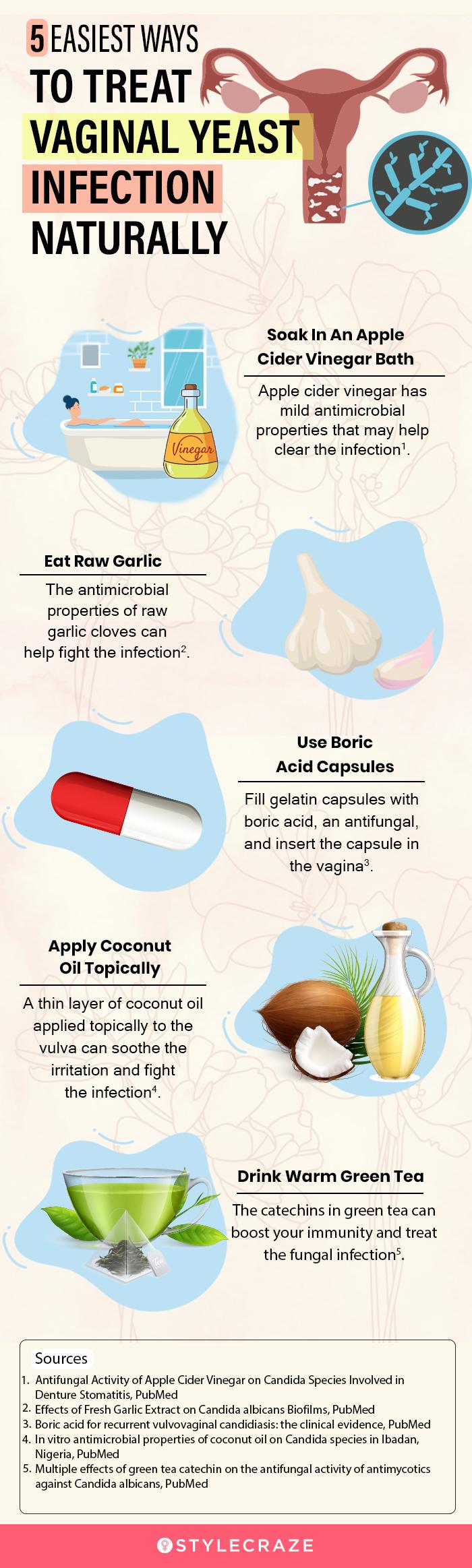
H4: Yeast Infections (Candidiasis)
Yeast infections, caused by an overgrowth of Candida fungus, are incredibly common. They can lead to intense itching, burning, and sometimes small, red bumps or a cottage cheese-like discharge. The vulva can become red and swollen.
H4: Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Several STIs can manifest as vaginal bumps. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent complications and transmission.
- Genital Herpes: Caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), genital herpes can cause painful blisters or sores that eventually break open and crust over. These can appear on the vulva, vagina, cervix, or anus.
- Genital Warts (HPV): Human Papillomavirus (HPV) can cause cauliflower-like growths or flesh-colored bumps on the vulva, vagina, or anus. Some strains of HPV are linked to cervical cancer, making vaccination and regular screenings important.
- Molluscum Contagiosum: This viral infection causes small, dome-shaped bumps with a central dimple. It’s contagious and can spread through skin-to-skin contact.
- Syphilis: In its primary stage, syphilis can present as a painless sore called a chancre. This sore can appear on the vulva, vagina, or cervix.
H3: Irritation and Allergic Reactions: Everyday Triggers
Sometimes, the cause of vaginal How to get rid of pimples faster your ultimate guide to clearer skin bumps is simpler – irritation from everyday products or an allergic reaction.
H4: Contact Dermatitis
This occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. Common culprits include:
- Soaps and Washes: Harsh soaps, scented feminine hygiene products, and douches can strip the natural protective oils from the vulvar skin, leading to dryness, redness, and bumps.
- Lubricants and Spermicides: Some individuals may be sensitive to ingredients in lubricants or spermicides used with condoms or other birth control methods.
- Detergents and Fabric Softeners: Residue from laundry products on underwear can cause irritation.
- Latex: For those with a latex allergy, condoms or diaphragms can trigger a reaction.
H4: Folliculitis
This is inflammation of the hair follicles, often caused by bacteria. It can appear as small, red bumps or pimple-like lesions, particularly in areas where hair is shaved or waxed.
H3: Non-Infectious Growths: Benign Variations
Not all bumps are a sign of infection or irritation. Some are harmless growths that are simply part of your body’s natural variations.
H4: Bartholin’s Cysts
Bartholin’s glands are located on either side of the vaginal opening and produce lubrication. If a gland becomes blocked, a cyst can form. These are usually painless unless they become infected, in which case they can form an abscess.
H4: Skin Tags
These are small, soft, flesh-colored growths that can appear anywhere on the body, including the vulva. They are benign and typically do not cause any discomfort.
H4: Sebaceous Cysts
These form when a sebaceous gland becomes blocked, leading to a sac filled with sebum (oil). They are usually painless and can be removed if they become bothersome.
H4: Fordyce Spots
These are tiny, harmless, yellowish-white bumps that are enlarged sebaceous glands. They can appear on the labia and are not a cause for concern.
H3: Hormonal Changes: A Natural Influence
Fluctuations in hormones can also play a role in the appearance of vaginal bumps.
H4: Puberty and Menstruation
During puberty, hormonal shifts can lead to increased oil production, potentially causing acne-like bumps on the vulva. Similarly, hormonal changes around menstruation can sometimes trigger breakouts.
H4: Pregnancy and Menopause
Hormonal shifts during pregnancy and menopause can also influence skin conditions, including the development of vaginal bumps.
When to Seek Professional Help: Crucial Steps for Treatment
While many vaginal bumps can be managed at home, it’s essential to know when to consult a healthcare professional. This is a critical aspect of understanding how to treat vaginal bumps safely and effectively.
- Persistent or Worsening Symptoms: If bumps don’t improve after a few days of home care or if they worsen, it’s time to see a doctor.
- Severe Pain or Discomfort: Intense pain, burning, or itching warrants medical attention.
- Unusual Discharge: A change in vaginal discharge, especially if it’s foul-smelling, discolored, or accompanied by bumps, should be evaluated.
- Fever or Chills: These systemic symptoms could indicate a more serious infection.
- Suspicion of STI: If you’ve had unprotected sex or are concerned about an STI, get tested and treated promptly.
- Bleeding: Any bleeding from the bumps or vaginal area that isn’t related to your menstrual cycle needs medical assessment.
- Recurrent Bumps: If you experience frequent occurrences of vaginal bumps, your doctor can help identify underlying causes and develop a long-term management plan.
Your doctor will likely perform a physical examination, ask about your medical history and sexual activity, and may recommend tests such as a pelvic exam, a swab for infection, or blood tests.
Effective Strategies: How to Treat Vaginal Bumps
The approach to how to treat vaginal bumps depends entirely on the underlying cause. Here’s a breakdown of common treatment strategies:
H3: Home Care and Comfort Measures
For mild irritation or bumps that are not due to infection, these measures can provide relief:
- Gentle Hygiene: Wash the vulvar area with plain, lukewarm water only. Avoid harsh soaps, perfumed products, and douches. Pat the area dry gently with a soft towel.
- Loose-Fitting Clothing: Wear breathable cotton underwear and avoid tight-fitting pants or synthetic fabrics that can trap moisture and cause irritation.
- Warm Compresses: For minor swelling or discomfort, a warm compress can be soothing.
- Avoid Scratching: While tempting, scratching can worsen inflammation and potentially lead to infection.
- Lukewarm Baths: Soaking in a plain, lukewarm bath can help cleanse and soothe the area. Avoid bubble baths or scented additives.
H3: Medical Treatments for Specific Conditions
When a diagnosis is made, your doctor will prescribe the appropriate treatment.
H4: Antibiotics for Bacterial Infections
If bacterial vaginosis or a bacterial infection is diagnosed, a course of oral or vaginal antibiotics will be prescribed. It’s crucial to complete the entire course of medication as directed.
H4: Antifungal Medications for Yeast Infections
Over-the-counter or prescription antifungal creams, suppositories, or oral medications are highly effective for yeast infections.
H4: Antiviral Medications for Viral Infections
For genital herpes, antiviral medications can help manage outbreaks, reduce their severity, and prevent transmission. There is no cure for herpes, but it can be effectively managed.
H4: Topical Treatments for Genital Warts
Genital warts can be treated with prescription topical medications, cryotherapy (freezing), or surgical removal.
H4: Topical Steroids or Antihistamines for Irritation
If contact dermatitis or general irritation is the cause, your doctor might recommend a mild topical corticosteroid cream or oral antihistamines to reduce inflammation and itching.
H4: Drainage or Excision for Cysts and Abscesses
Bartholin’s cysts or abscesses may require drainage by a healthcare professional. Larger or persistent cysts might need surgical removal. Sebaceous cysts can also be surgically removed if they become problematic.
H3: Lifestyle Adjustments for Prevention
Preventing future occurrences is a key component of managing vaginal health and understanding how to treat vaginal bumps in the long run.
- Practice Safe Sex: Consistent and correct use of condoms significantly reduces the risk of STIs.
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regular, gentle cleansing of the vulvar area is important.
- Choose Breathable Fabrics: Opt for cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothing.
- Avoid Irritants: Be mindful of the products you use on your genital area. Opt for unscented, hypoallergenic options.
- Stay Hydrated and Eat a Balanced Diet: General health contributes to overall well-being, including skin health.
- Manage Stress: High stress levels can sometimes impact the immune system and skin health.
Dispelling Myths and Building Confidence
It’s important to approach vaginal health with a sense of normalcy and understanding. Vaginal bumps are a common experience, and seeking information and care is a sign of self-advocacy. Don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider. They are there to provide support, accurate information, and effective solutions for how to treat vaginal bumps and maintain optimal vaginal health.
Frequently Asked Questions About Vaginal Bumps
Q1: Are vaginal bumps always a sign of an STI?
A1: No, absolutely not. While some STIs can cause vaginal bumps, many other conditions, such as folliculitis, cysts, or irritation, are not sexually transmitted.
Q2: Can I treat vaginal bumps at home?
A2: For mild irritation or bumps that are clearly not infected, some home care measures like gentle cleansing and loose clothing can provide relief. However, it’s crucial to consult a doctor if you’re unsure of the cause or if symptoms persist or worsen.
Q3: How can I prevent vaginal bumps?
A3: Prevention involves practicing safe sex, maintaining good hygiene with gentle products, wearing breathable clothing, and avoiding known irritants.
Q4: When should I see a doctor about vaginal bumps?
A4: You should see a doctor if you experience severe pain, unusual discharge, fever, or if the bumps don’t improve with home care or are recurrent.
Q5: Are Bartholin’s cysts dangerous?
A5: Bartholin’s cysts are usually benign. They can become uncomfortable or infected, in which case medical attention is needed for drainage or treatment.
Q6: Can stress cause vaginal bumps?
A6: While stress doesn’t directly cause bumps, it can weaken the immune system, potentially making you more susceptible to infections that might lead to bumps.
Embrace Your Well-being: Your Journey to Relief
Understanding how to treat vaginal bumps is a powerful step towards reclaiming your comfort and confidence. By arming yourself with knowledge about the diverse causes and effective treatment options, you can navigate these concerns with greater ease and assurance. Remember, your vaginal health is an integral part of your overall well-being. If you’ve found this guide helpful, please share it with others who might benefit from this empowering information! Let’s foster open conversations and a supportive environment for all aspects of women’s health.






