Unveiling the Secrets to Banishing Bothersome Blemishes: How to Treat Pimples with Pus Effectively!
Ah, the dreaded pimple with pus. It’s a common, yet incredibly frustrating, unwelcome guest that can appear at the most inconvenient times, casting a shadow over our confidence. Whether it’s a sudden eruption before a big event or a persistent cluster, understanding how to treat pimples with pus is crucial for achieving and maintaining clear, radiant skin. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and actionable steps to tackle these stubborn blemishes, transforming your skincare routine from a battleground to a celebration of healthy skin.
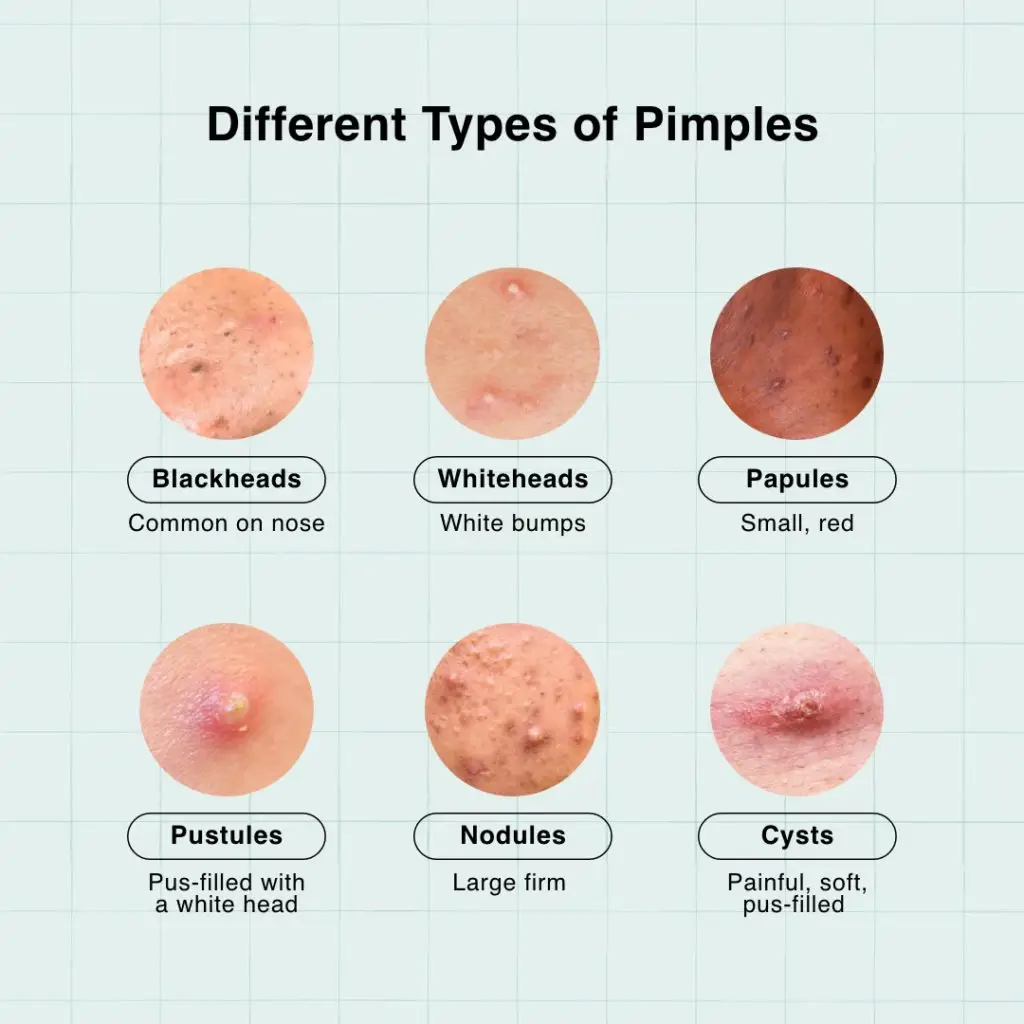
Pimples with pus, often referred to as pustules, are a type of inflammatory acne. They’re characterized by a red, inflamed base topped with a white or yellowish head, indicating the presence of sebum, bacteria, and white blood cells fighting off infection. While they can be tempting to pick at (we’ve all been there!), doing so can lead to scarring, increased inflammation, and further breakouts. The good news is that with the right approach, you can effectively manage and treat these unwelcome visitors, paving the way for smoother, clearer skin.
Understanding the Enemy: What Causes Pimples with Pus?
Before we dive into the solutions, let’s briefly understand the culprits behind those pesky pustules. The formation of pimples with pus is a multi-faceted process involving:
- Excess Sebum Production: Our skin naturally produces an oily substance called sebum to keep it moisturized. However, overproduction can clog pores.
- Dead Skin Cells: These can accumulate and mix with sebum, further blocking hair follicles.
- Bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes – P. acnes): This bacteria naturally lives on our skin but can thrive in clogged pores, leading to inflammation and infection.
- Inflammation: The body’s immune response to the bacteria and blockage results in the redness and swelling characteristic of pimples.
When these factors combine, they create an environment ripe for pustule formation. Understanding this helps us appreciate why certain treatments are more effective than others.
Your Arsenal of Solutions: How to Treat Pimples with Pus Safely and Effectively
Navigating the world of skincare can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re dealing with active breakouts. Fear not! We’ve curated a list of tried-and-true methods for how to treat pimples with pus, focusing on gentle yet powerful approaches.
H3: The Gentle Touch: Cleansing and Exfoliation
A cornerstone of any effective skincare routine, proper cleansing is paramount when dealing with pimples.
H4: Gentle Cleansing for Pustule-Prone Skin
- Choose the Right Cleanser: Opt for a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser that won’t strip your skin of its natural oils. Look for ingredients like salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide in lower concentrations for gentle exfoliation and antibacterial properties. Avoid harsh soaps or scrubs that can irritate inflamed skin.
- Frequency is Key: Cleanse your face twice daily – once in the morning and once before bed. Over-cleansing can actually worsen inflammation.
- Technique Matters: Use lukewarm water and your fingertips to gently massage the cleanser into your skin. Avoid using rough washcloths or loofahs, which can aggravate pustules. Pat your skin dry with a clean, soft towel.
H4: The Power of Exfoliation (with Caution!)
Exfoliation helps remove dead skin cells that can contribute to pore blockages. However, when treating pimples with pus, it’s essential to be gentle.
- Chemical Exfoliants: Beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs) like salicylic acid are particularly effective for acne as they are oil-soluble and can penetrate pores to unclog them. Alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid can also help, but may be more irritating to inflamed skin. Start with a low concentration and use them a few times a week.
- Physical Exfoliants (Use Sparingly): If you prefer physical exfoliation, opt for very fine-grained scrubs and use them with extreme gentleness. Avoid harsh particles that can create micro-tears in the skin. It’s often best to stick to chemical exfoliants when dealing with active pustules.
H3: Targeted Treatments: Topical Solutions
Once your skin is clean, it’s time to bring in the heavy hitters – topical treatments designed to combat bacteria and reduce inflammation.
H4: The Magic of Benzoyl Peroxide
Benzoyl peroxide is a potent antibacterial agent that kills P. acnes bacteria and helps to reduce inflammation. It’s available in various strengths, from over-the-counter options (2.5% to 10%) to prescription formulations.
- How to Use: Apply a thin layer to the affected areas after cleansing. Start with a lower concentration (2.5% or 5%) to minimize dryness and irritation. You can gradually increase the strength if your skin tolerates it.
- Potential Side Effects: Benzoyl peroxide can cause dryness, redness, and peeling. It can also bleach fabrics, so be mindful of your pillowcases and towels.
H4: Salicylic Acid: The Pore-Penetrating Hero
Salicylic acid is a BHA that exfoliates the skin and penetrates deep into pores to dissolve sebum and dead skin cells. This makes it excellent for preventing and treating clogged pores that lead to pustules.
- How to Use: Available in cleansers, toners, serums, and spot treatments. Apply as directed on the product packaging.
- Benefits: It’s generally less irritating than benzoyl peroxide and can help to reduce redness and swelling.
H4: Sulfur: A Gentle Yet Effective Option
Sulfur has been used for centuries to treat skin conditions. It helps to dry out excess oil and has mild antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
- How to Use: Often found in masks, spot treatments, and cleansers. It has a distinct smell, but its effectiveness often outweighs this.
- Good for Sensitive Skin: Sulfur is generally well-tolerated by sensitive skin types.
H4: Topical Antibiotics (Prescription Only)
For more severe or persistent pustules, a dermatologist may prescribe topical antibiotics like clindamycin or erythromycin. These medications work by killing bacteria and reducing inflammation.
- Important Note: Topical antibiotics should be used as directed by your doctor and are often prescribed in combination with other treatments to prevent antibiotic resistance.
H3: The Golden Rule: NEVER Pick or Pop!
This is perhaps the most crucial piece of advice when it comes to how to treat pimples with pus. We understand the urge is strong, but resist it with all your might!
- Why Picking is Bad:
- Increased Inflammation: You introduce more bacteria and further irritate the skin, making the pimple redder and more swollen.
- Scarring: Picking can damage the deeper layers of the skin, leading to permanent acne scars, including hyperpigmentation (dark spots) and indented scars.
- Spreading Infection: You can spread the bacteria to other areas of your face, causing new breakouts.
- Longer Healing Time: Picking can prolong the healing process of the existing pimple.
Instead of picking, consider using a pimple patch (hydrocolloid patch). These discreet patches can help to absorb excess fluid from the pimple, protect it from bacteria and dirt, and prevent you from picking. They can also create a moist healing environment, which can speed up the process.
H3: Home Remedies: What Works and What Doesn’t
While scientific treatments are often the most reliable, some natural remedies can offer gentle support.
H4: The Soothing Power of Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil has natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
- How to Use: Always dilute tea tree oil with a carrier oil (like jojoba or coconut oil) before applying it to your skin. A common dilution is 1-2 drops of tea tree oil per teaspoon of carrier oil. Apply a small amount to the affected area with a cotton swab.
- Patch Test: It’s essential to do a patch test on a small area of your skin first to ensure you don’t have an adverse reaction.
H4: Honey: Nature’s Antibacterial Balm
Raw honey, particularly Manuka honey, possesses antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
- How to Use: Apply a small dab of raw honey directly to the pimple and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing with lukewarm water.
H4: Green Tea Compress
Green tea is rich in antioxidants and has anti-inflammatory properties.
- How to Use: Brew a cup of green tea, let it cool, and then soak a cotton ball or cloth in the tea. Gently apply it to the pimple for a few minutes.
Important Note on Home Remedies: While these can be helpful, they are generally not as potent as scientifically formulated acne treatments. They are best used as supplementary treatments or for very mild breakouts.
H3: Lifestyle Factors: Supporting Your Skin from Within
Skincare isn’t just about what you put on your face; it’s also about how you live.
H4: Diet and Hydration
- Balanced Diet: While the link between diet and acne is complex and varies from person to person, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall skin health. Limiting processed foods, excessive sugar, and dairy may be beneficial for some individuals.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and aiding in the body’s natural detoxification processes.
H4: Stress Management
Stress can trigger hormonal fluctuations that may exacerbate acne. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time in nature, can have a positive impact on your skin.
H4: Sleep Hygiene
Adequate sleep is vital for skin repair and regeneration. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
H4: Hygiene Habits
- Clean Your Phone: Your phone screen can harbor a surprising amount of bacteria. Wipe it down regularly with an antibacterial wipe.
- Change Pillowcases: Change your pillowcases frequently (at least twice a week) to prevent the buildup of oil and bacteria.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Resist the urge to touch your face throughout the day, as this can transfer dirt and bacteria.
H3: When to Seek Professional Help
While many pimples with pus can be managed at home, there are times when professional intervention is necessary.
H4: Consulting a Dermatologist
If you experience any of the following, it’s time to schedule an appointment with a dermatologist:
- Severe or Persistent Acne: If your acne is widespread, deeply inflamed, or doesn’t improve with over-the-counter treatments.
- Painful Cysts or Nodules: These are deeper, more severe forms of acne that require professional care.
- Concerns about Scarring: A dermatologist can offer treatments to prevent or minimize scarring.
- Sudden Onset of Acne: A sudden change in your skin can sometimes indicate an underlying medical condition.
A dermatologist can assess your specific skin type and concerns, diagnose the cause of your acne, and recommend a personalized treatment plan, which may include prescription-strength topical medications, oral medications, or in-office procedures.
Festive Finale: Celebrating Your Journey to Clearer Skin!
Tackling pimples with pus can feel like a marathon, but with the right knowledge and consistent effort, you can achieve the clear, radiant skin you deserve. Remember to be patient with yourself and your skin. Every step you take towards a consistent and gentle skincare routine is a victory.
Embrace the power of informed choices, celebrate small victories, and don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance when needed. Your skin is a beautiful canvas, and with the right care, it will shine!
Frequently Asked Questions About How to Treat Pimples with Pus
Q1: How quickly can I expect to see results when treating pimples with pus?
Results vary depending on the severity of the pimple and the treatment used. With targeted treatments like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, you might start to see a reduction in redness and swelling within a few days. However, complete healing can take a week or more. Consistency is key!
Q2: Can I use toothpaste to treat pimples with pus?
While some people swear by toothpaste, it’s generally not recommended. Toothpaste contains ingredients that can be highly irritating and drying to the skin, potentially worsening inflammation and leading to redness, peeling, How to get rid of butt zits banish blemishes for good and even burns. Stick to scientifically proven acne treatments.
Q3: What is the best way to prevent pimples with pus from forming?
Consistent cleansing with a gentle, acne-fighting cleanser, regular exfoliation (as tolerated), and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help prevent breakouts. Identifying and avoiding personal triggers, such as certain foods or stress, can also be beneficial.
Q4: Are pimple patches effective for pimples with pus?
Yes, pimple patches, particularly hydrocolloid patches, can be very effective. They help to absorb excess fluid, protect the pimple from external contaminants, prevent picking, and create a moist healing environment, which can speed up the healing process.
Q5: How do I know if my pimple is infected and needs medical attention?
Signs of a potential infection include increased redness, swelling, warmth, throbbing pain, and the presence of pus that is green or has a foul odor. If you suspect an infection, it’s best to consult a doctor or dermatologist.
Q6: Can I wear makeup when I have pimples with pus?
Yes, you can wear makeup, but it’s crucial to choose non-comedogenic, oil-free products. Always remove your makeup thoroughly before bed to prevent pore blockages. Consider mineral-based makeup, which tends to be less irritating.
Q7: Is it okay to use hot compresses on pimples with pus?
A warm compress can sometimes help to bring a pimple to a head, making it easier for the pus to drain naturally. However, use caution and avoid excessively hot temperatures, which can burn the skin. Gently apply a warm, damp cloth for a few minutes. Do not attempt to squeeze after using a compress.
Q8: How does diet affect pimples with pus?
The link between diet and acne is complex and individual. For some, high-glycemic foods, dairy, or certain fats may exacerbate breakouts. Focusing on a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and staying hydrated is generally beneficial for skin health.
Q9: Can stress cause pimples with pus?
Yes, stress can contribute to acne breakouts. When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones like cortisol, which can increase oil production and inflammation, potentially leading to pimples. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can be helpful.
Q10: What’s the difference between a pimple with pus and a blackhead or whitehead?
Pimples with pus (pustules) are inflamed lesions with a visible head containing pus. Blackheads are open comedones where the pore is clogged but exposed to air, causing the sebum to oxidize and appear black. Whiteheads are closed comedones where the pore is clogged but covered by a thin layer of skin, appearing as a small white bump. Pustules are a more advanced stage of inflammatory acne.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-acne-pustule-15579-FINAL-4996720e595a4444b7ea0be583174429.jpg)