Discover the ultimate secrets on how to get rid of white bumps on your face and reclaim your radiant complexion! Are you tired of those stubborn little white spots that mar your otherwise smooth skin? You’re not alone. These common blemishes, often mistaken for acne, can be a source of frustration for many. But fear not! This comprehensive guide will illuminate the causes, effective treatments, and preventative measures to help you achieve the clear, glowing skin you deserve.
Understanding the Culprits: What Exactly Are Those White Bumps?
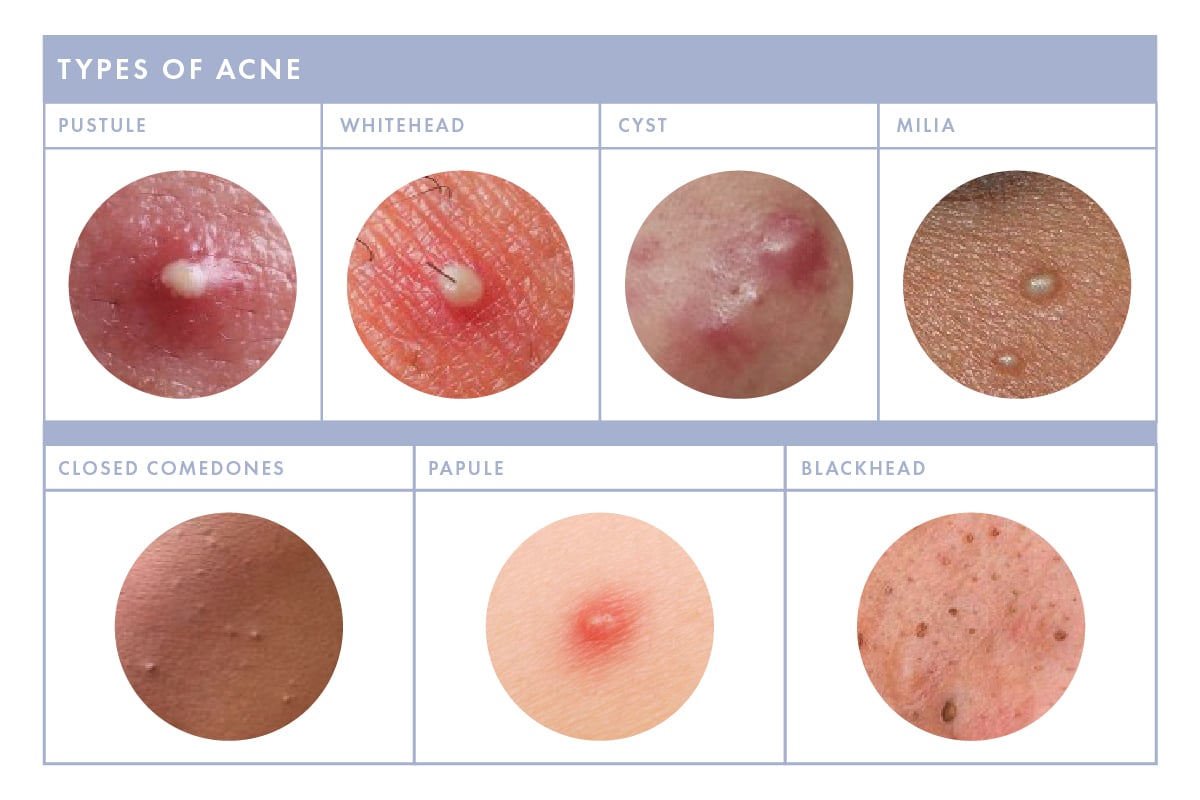
Before we dive into solutions, it’s crucial to understand what we’re dealing with. Those pesky white bumps on your face aren’t always what they seem. While sometimes they can be a form of acne, more often than not, they point to different underlying skin conditions. Let’s explore the most common culprits:
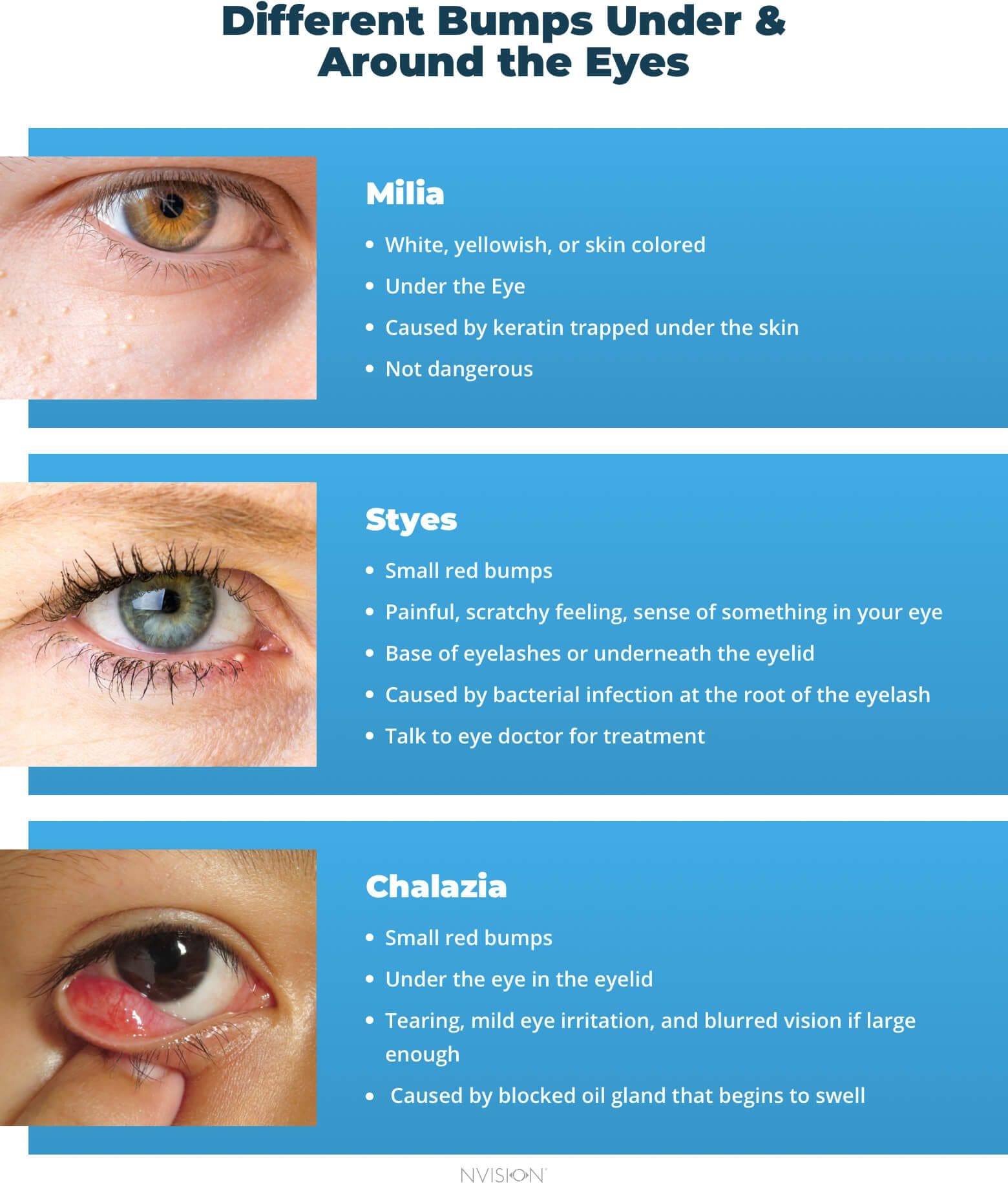
Milia: The Tiny White Pearls
Milia, often referred to as "milk spots," are small, pearly white cysts that typically appear on the face, especially around the eyes and cheeks. They are essentially tiny pockets of keratin, a protein found in skin and hair, trapped beneath the surface.
- Causes of Milia:
- Dead Skin Cell Buildup: When dead skin cells don’t shed properly, they can become trapped, forming milia.
- Sun Damage: Prolonged sun exposure can thicken the outer layer of the skin, making it harder for dead cells to escape.
- Skin Injury: Minor injuries like burns, blisters, or even harsh exfoliation can trigger milia formation.
- Certain Skincare Products: Heavy, occlusive creams or products containing certain ingredients can clog pores and contribute to milia.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be more predisposed to developing milia.
Closed Comedones (Whiteheads): The Early Stage of Acne
Whiteheads are a non-inflammatory form of acne. They occur when a hair follicle becomes clogged with excess sebum (oil), dead skin cells, and bacteria. Unlike blackheads, the pore remains closed, trapping the contents beneath the skin’s surface, giving it that characteristic white appearance.
- Causes of Whiteheads:
- Excess Sebum Production: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, menstruation, or stress, can increase oil production.
- Dead Skin Cell Accumulation: Similar to milia, a buildup of dead skin cells can clog pores.
- Bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes): This bacteria thrives in clogged follicles and contributes to inflammation.
- Diet: While controversial, some studies suggest that high-glycemic foods and dairy might exacerbate acne for some individuals.
- Friction and Pressure: Wearing tight clothing, helmets, or even resting your face on your hands can irritate the skin and lead to breakouts.
Fordyce Spots: Harmless but Noticeable
Fordyce spots are tiny, harmless, raised bumps that appear as small, pale yellow or white dots. They are essentially enlarged sebaceous glands that lack a hair follicle. They commonly appear on the lips, inside the cheeks, and on the genitals. While they are not a medical concern, their appearance can be bothersome for some.
- Causes of Fordyce Spots:
- Enlarged Sebaceous Glands: This is the primary cause, and it’s often a natural variation in skin structure.
- Hormonal Influences: They can become more prominent during puberty due to hormonal changes.
Acne Vulgaris (Cystic Acne): Deeper, More Painful Bumps
While not exclusively white, deeper, inflamed bumps can sometimes have a white or yellowish head. Cystic acne forms when a pore becomes severely inflamed and infected, leading to large, painful lumps beneath the skin’s surface.
- Causes of Cystic Acne:
- Severe Inflammation: A combination of excess oil, dead skin cells, bacteria, and a strong inflammatory response.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Significant hormonal shifts can trigger severe acne.
- Genetics: A family history of severe acne increases your risk.
Your Arsenal of Solutions: How to Get Rid of White Bumps on Your Face Effectively
Now that we’ve identified the potential culprits, let’s explore the most effective strategies for how How do you get rid of pimples conquer stubborn breakouts to get rid of white bumps on your face. The key is to tailor your approach to the specific type of bump you’re experiencing.
Targeting Milia: Gentle Exfoliation and Professional Help
Since milia are caused by trapped keratin, gentle exfoliation is your best friend.
-
Gentle Chemical Exfoliation:
- Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): Glycolic acid and lactic acid are excellent for dissolving dead skin cells. Look for cleansers, toners, or serums containing these ingredients. Start with a lower concentration and use them a few times a week to avoid irritation.
- Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs): Salicylic acid is oil-soluble, meaning it can penetrate pores and help unclog them. It’s particularly effective if your milia are accompanied by oily skin.
-
Physical Exfoliation (Use with Caution):
- While gentle physical exfoliants like finely ground oatmeal or konjac sponges can be used, avoid harsh scrubs with large, jagged particles, as these can irritate the skin and potentially worsen the problem.
-
Professional Extraction:
- For stubborn milia, a dermatologist or licensed esthetician can safely extract them using a sterile needle or lancet. Never attempt to squeeze or pop milia yourself, as this can lead to infection, scarring, and inflammation.
-
Retinoids:
- Topical retinoids (like retinol or prescription tretinoin) can help increase cell turnover, preventing dead skin cells from accumulating and trapping keratin. Start with a low concentration and gradually increase as your skin tolerates it.
Conquering Whiteheads: A Multi-Pronged Approach
Treating whiteheads involves a combination of cleansing, exfoliation, and oil control.
-
Consistent Cleansing:
- Wash your face twice daily with a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser. This removes excess oil, dirt, and impurities that can clog pores.
-
Exfoliation is Key:
- Salicylic Acid (BHA): As mentioned, salicylic acid is a powerhouse for whiteheads. Use a cleanser, toner, or spot treatment containing salicylic acid to penetrate pores and dissolve blockages.
- Benzoyl Peroxide: This ingredient kills acne-causing bacteria and helps to dry out pimples. It can be found in washes, creams, and spot treatments. Start with a lower concentration (2.5% or 5%) to minimize dryness and irritation.
-
Spot Treatments:
- For individual whiteheads, a targeted spot treatment can be very effective. Look for products containing salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, or sulfur.
-
Clay Masks:
- Clay masks, such as bentonite or kaolin clay, can help absorb excess oil and impurities from the pores, making them a great addition to your weekly routine.
-
Moisturize Wisely:
- Even oily, acne-prone skin needs hydration. Opt for lightweight, oil-free, non-comedogenic moisturizers to prevent your skin from overcompensating and producing more oil.
Managing Fordyce Spots: Focus on Appearance, Not Treatment
Since Fordyce spots are a natural variation, the focus is on managing their appearance rather than eliminating them.
-
Cosmetic Treatments (for significant concerns):
- Laser Therapy: Certain laser treatments can help reduce the appearance of Fordyce spots.
- Topical Retinoids: In some cases, topical retinoids may help to minimize their visibility.
- Electrocautery: This procedure uses heat to destroy the enlarged sebaceous glands.
-
Camouflage:
- For those who find them bothersome, makeup can be used to conceal Fordyce spots.
Addressing Cystic Acne: Professional Intervention is Crucial
Cystic acne is a more severe form of acne and often requires professional medical attention.
-
Dermatologist Consultation:
- A dermatologist can diagnose the severity of your cystic acne and recommend the most effective treatment plan.
-
Prescription Medications:
- Topical Antibiotics: To reduce bacteria and inflammation.
- Oral Antibiotics: For more widespread or severe cases.
- Isotretinoin (Accutane): A powerful oral medication that significantly reduces oil production and inflammation, often used for severe, persistent cystic acne. This requires close medical supervision.
- Hormonal Therapy: For women, oral contraceptives or spironolactone may be prescribed to regulate hormones.
-
Corticosteroid Injections:
- For large, painful cysts, a dermatologist can inject a corticosteroid directly into the lesion to quickly reduce inflammation and pain.
Prevention is Better Than Cure: Strategies for Long-Term Clarity
Once you’ve successfully tackled those white bumps, maintaining clear skin is paramount. Here are some proactive steps to prevent their return:
Establish a Consistent Skincare Routine:
- Cleanse Daily: Wash your face morning and night with a gentle cleanser.
- Exfoliate Regularly (but not excessively): Incorporate chemical exfoliants 2-3 times a week, depending on your skin’s tolerance.
- Moisturize: Even oily skin needs hydration. Choose lightweight, non-comedogenic formulas.
- Use Sunscreen Daily: Protect your skin from sun damage, which can contribute to milia and worsen acne.
Choose Your Products Wisely:
- "Non-Comedogenic" is Your Mantra: Look for skincare and makeup products labeled "non-comedogenic" or "oil-free" to avoid clogging pores.
- Patch Test New Products: Before applying a new product all over your face, test it on a small, inconspicuous area to check for any adverse reactions.
Lifestyle Habits for Healthier Skin:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your skin hydrated from within.
- Balanced Diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods. While the link between diet and acne is complex, a healthy diet generally benefits skin health.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can wreak havoc on your hormones and skin. Explore stress-management techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Your hands carry bacteria and oils that can transfer to your face and clog pores.
- Clean Your Phone and Pillowcases: Regularly clean your phone screen and change your pillowcases to minimize bacteria transfer.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many white bumps can be managed at home, it’s important to know when to consult a professional.
- Persistent or Worsening Bumps: If your white bumps don’t improve with home treatments or are becoming more numerous or inflamed.
- Painful or Infected Bumps: Any bumps that are red, swollen, painful, or show signs of infection (pus, warmth).
- Scarring: If you are concerned about scarring from previous breakouts.
- Sudden Onset of Severe Acne: A sudden, severe breakout could indicate an underlying medical condition.
A dermatologist can provide accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and access to prescription medications that are often necessary for more stubborn or severe cases.
Frequently Asked Questions About White Bumps on Your Face
Q1: Can I pop white bumps on my face?
A1: It’s generally not recommended to pop white bumps, especially milia, as this can lead to infection, inflammation, and scarring. For whiteheads, while tempting, popping can push bacteria deeper into the pore. It’s best to use targeted treatments or seek professional extraction.
Q2: How long does it take to get rid of white bumps?
A2: The timeline varies depending on the type and severity of the bumps. Milia can take weeks to months to resolve with consistent treatment. Whiteheads may start to improve within a few days to a week with appropriate skincare. Severe acne may require longer treatment durations.
Q3: Are white bumps contagious?
A3: No, white bumps like milia and whiteheads are not contagious. They are caused by internal factors related to skin cell turnover, oil production, or trapped keratin.
Q4: Can diet cause white bumps on my face?
A4: While the direct link is debated, for some individuals, certain dietary factors like high-glycemic foods or dairy may exacerbate acne breakouts. Focusing on a balanced, whole-foods diet is generally beneficial for skin health.
Q5: What’s the difference between milia and whiteheads?
A5: Milia are small, firm cysts caused by trapped keratin, typically appearing as pearly white bumps. Whiteheads are a type of acne, occurring when a pore is clogged with oil and dead skin cells, and the pore remains closed.
Embrace Your Journey to Radiant Skin!
Dealing with white bumps on your face can feel disheartening, but with the right knowledge and a consistent approach, you can absolutely achieve clearer, smoother skin. Remember, patience and dedication are key. Embrace the journey of understanding your skin and discovering what works best for you.
Have you found success with any of these methods for how to get rid of white bumps on your face? Share your tips and experiences in the comments below! Let’s inspire each other to glow!
.jpg)