Ever noticed those perplexing little red, purple, or even brownish spots appearing just beneath your skin’s surface? These tiny discolored patches, often a source of concern and curiosity, can range from harmless everyday occurrences to indicators of something more significant. While often benign, their sudden appearance or persistence can leave us wondering: what are they, why are they here, and most importantly, how to get rid of blood spots under skin?
Fear not! This comprehensive guide is here to illuminate the mystery behind these intriguing skin marks. We’ll delve into their various forms, uncover the common culprits behind their appearance, and explore a spectrum of effective strategies – from soothing home remedies to advanced medical interventions – to help you understand and manage them. Get ready to embark on a journey to clearer, healthier-looking skin, armed with the knowledge to confidently address those pesky blood spots.
Unraveling the Mystery: What Exactly Are Blood Spots Under the Skin?
Before we dive into how to get rid of blood spots under skin, it’s essential to understand what these spots truly are. Essentially, blood spots under the skin, medically known as purpura, are a result of tiny blood vessels (capillaries) breaking and leaking blood into the surrounding tissue. This leakage causes the characteristic discoloration that we see on the skin’s surface. Depending on their size and cause, they can manifest in different ways:
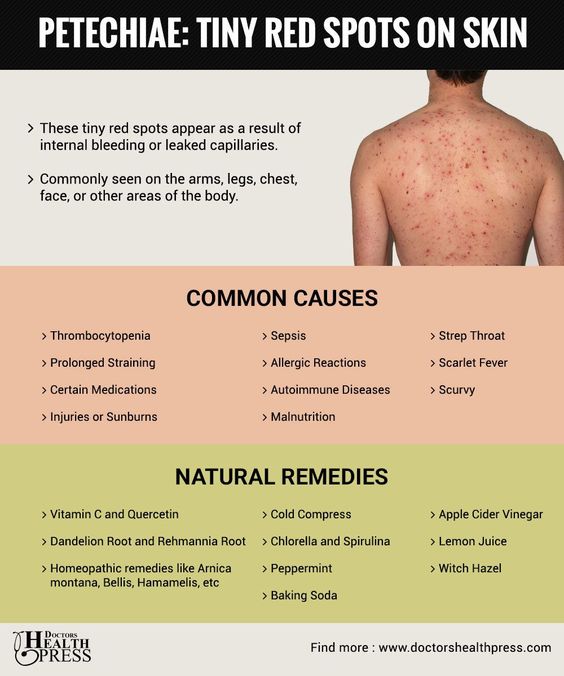
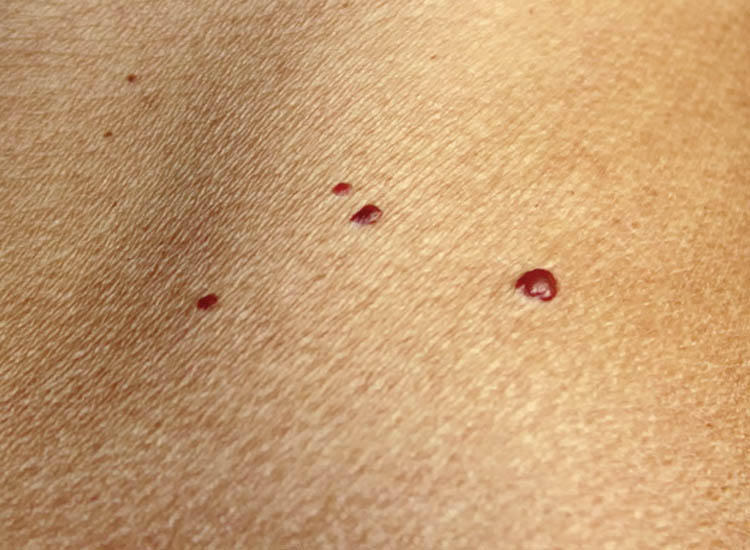
Petechiae: The Tiny Red Dots
These are pinpoint-sized (less than 2 millimeters in diameter) red, purple, or brown spots that often appear in clusters. They don’t lose their color when pressed (non-blanching), which distinguishes them from rashes. Petechiae are a common form of blood spots and are usually a sign of minor capillary damage.
Purpura: Larger Patches
Purpura refers to blood spots larger than petechiae, typically ranging from 2 millimeters to 1 centimeter in diameter. These spots can appear as red, purple, or even blackish-blue patches. They also do not blanch under pressure. Purpura can be a sign of more significant bleeding under the skin compared to petechiae.
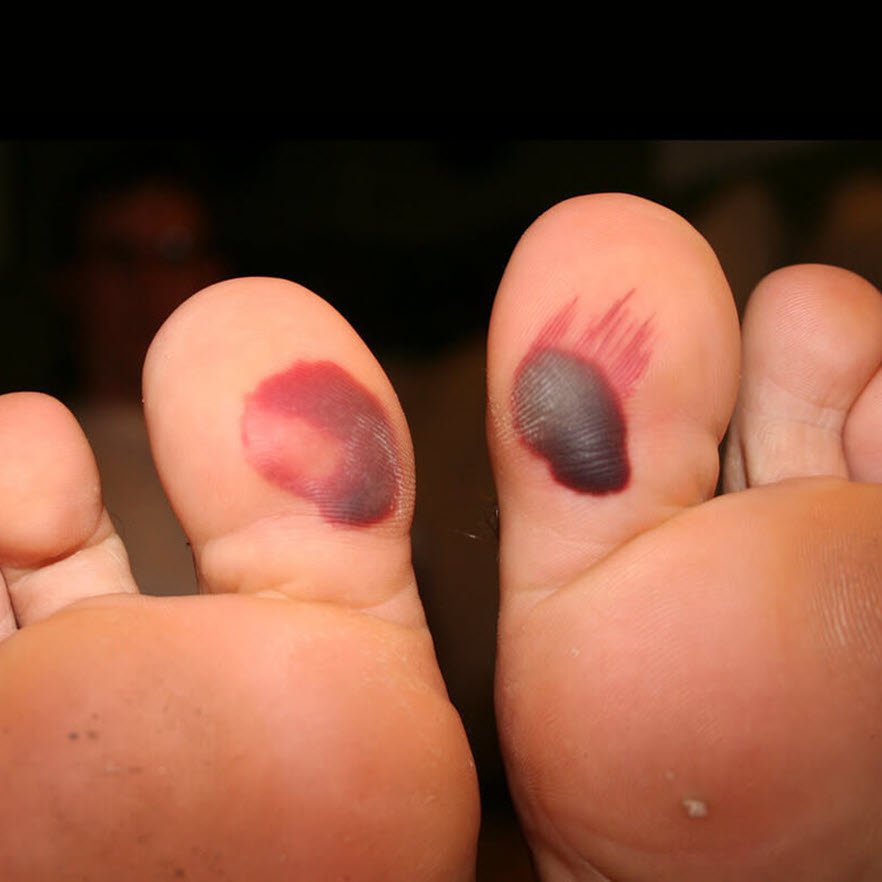
Ecchymosis: The Familiar Bruise
When blood spots are larger than 1 centimeter, they are generally classified as ecchymosis, more commonly known as a bruise. Bruises are usually caused by trauma and can change color over several days as the blood is reabsorbed by the body, progressing from red/purple to green, yellow, and brown before fading.
The Science Behind the Spots: Capillary Damage
At the heart of all these blood spots is the delicate network of capillaries. These are the smallest blood vessels in your body, responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products. When these fragile vessels are damaged, whether by physical force, inflammation, or underlying conditions, blood leaks out, creating the visible spots under the skin. Understanding this fundamental mechanism is the first step in learning how to get rid of blood spots under skin.
Common Culprits: Why Do These Blood Spots Appear?
The appearance of blood spots under the skin can be attributed to a wide array of factors, ranging from the utterly mundane to more serious medical conditions. Identifying the cause is often crucial for determining the most effective approach to how to get rid of blood spots under skin.
Everyday Trauma and Injury
This is by far the most common reason for blood spots, especially ecchymosis (bruises). Bumping into furniture, a fall, or even vigorous exercise can cause capillaries to rupture. Petechiae can sometimes appear after intense coughing, vomiting, or straining, as these actions temporarily increase pressure in the small blood vessels.
Medications and Their Side Effects
Certain medications can thin the blood or affect its clotting ability, making individuals more prone to developing blood spots.
- Anticoagulants (Blood Thinners): Warfarin, heparin, and newer oral anticoagulants are designed to prevent blood clots but can increase bruising.
- Antiplatelet Drugs: Aspirin, clopidogrel, and ibuprofen can also interfere with blood clotting.
- Corticosteroids: Long-term use of oral or topical steroids can thin the skin, making capillaries more fragile and susceptible to damage.
Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of certain vitamins can weaken blood vessels or impair clotting, leading to easier bruising and blood spots.
- Vitamin C Deficiency: Scurvy, though rare today, is characterized by widespread purpura due as Vitamin C is essential for collagen production, which strengthens blood vessel walls.
- Vitamin K Deficiency: Vitamin K plays a vital role in blood clotting. A deficiency can lead to excessive bleeding and bruising.
Allergic Reactions and Inflammatory Conditions
Sometimes, blood spots can be a manifestation of an allergic reaction or an inflammatory process affecting the blood vessels (vasculitis). Conditions like Henoch-Schönlein purpura, a form of vasculitis, cause small blood vessels to become inflamed and leak, leading to purpuric spots, often on the legs and buttocks.
Infections (Viral, Bacterial)
Severe infections can sometimes lead to blood spots.
- Viral Infections: Dengue fever, measles, rubella, and even severe cases of influenza can sometimes cause petechiae.
- Bacterial Infections: Sepsis or meningococcemia (a severe bacterial infection) can cause widespread purpura and petechiae, indicating a serious medical emergency.
Aging Skin: A Natural Occurrence
As we age, our skin naturally thins, and the protective fatty layer beneath it diminishes. Our blood vessels also become more fragile. This makes older adults more susceptible to senile purpura, where even minor bumps can cause large, flat, purple patches, often on the forearms and hands. These are generally harmless but can be aesthetically bothersome.
Underlying Medical Conditions
In some cases, blood spots can be a symptom of a more serious underlying health issue.
- Bleeding Disorders: Conditions like hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, or platelet disorders (e.g., thrombocytopenia, where platelet count is low) can significantly impair blood clotting, leading to easy bruising and spontaneous blood spots.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune conditions can sometimes cause vasculitis, leading to purpura.
- Liver Disease: A severely compromised liver can affect the production of clotting factors, leading to increased bleeding and bruising.
- Cancers: Certain blood cancers, like leukemia, can affect platelet production or function, resulting in widespread petechiae and purpura.
Understanding these diverse causes is fundamental. While many blood spots are benign, some warrant prompt medical attention.
When to Seek Professional Help: Don’t Ignore the Signs
While many blood spots are harmless and resolve on their own, it’s crucial to know when to consult a healthcare professional. Ignoring certain signs could delay diagnosis of a potentially serious underlying condition. Knowing when to seek medical advice is a key part of learning how to get rid of blood spots under skin safely and effectively.
Sudden Onset and Widespread Spots
If you suddenly develop numerous petechiae or purpura over a large area of your body, especially without any apparent injury, it’s a red flag. This could indicate a systemic issue that needs immediate investigation.
Accompanying Symptoms
Be particularly vigilant if blood spots are accompanied by other symptoms such as:
- Fever, chills, or other signs of infection
- Severe headache or stiff neck
- Unexplained fatigue or weakness
- Easy bleeding from gums or nosebleeds
- Swelling or pain in joints
- Significant abdominal pain
- Changes in consciousness or confusion
These symptoms, especially with widespread petechiae, could point to serious conditions like meningitis or sepsis, which require urgent medical attention.
Spots That Don’t Fade
Most bruises and minor blood spots gradually fade over days to weeks. If a blood spot persists for an unusually long time (several weeks or months) without any signs of improvement, or if it changes in size or appearance, it’s wise to have it checked by a doctor.
Known Bleeding Disorders
If you have a diagnosed bleeding disorder or are on anticoagulant medication, any new or unusual blood spots should be reported to your doctor, as it might indicate an adjustment in your treatment plan or a complication.
Navigating Your Options: How to Get Rid of Blood Spots Under Skin Effectively
Once you understand the cause and have ruled out serious underlying conditions, you can explore various strategies for how to get rid of blood spots under skin. The approach will largely depend on the size, severity, and cause of the spots.
First Aid & Home Remedies for Minor Spots
For common bruises and minor blood spots resulting from trauma, several home remedies can help accelerate healing and reduce their appearance.
- RICE Method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation): This classic first-aid approach is highly effective for fresh bruises.
- Rest: Avoid activities that might further injure the area.
- Ice: Apply a cold pack or ice wrapped in a cloth to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day during the first 24-48 hours. This constricts blood vessels, reducing blood leakage and swelling.
- Compression: Gently wrap the area with an elastic bandage to help prevent further swelling.
- Elevation: Keep the bruised area elevated above your heart to reduce blood flow to the site and minimize swelling.
- Topical Creams: Arnica, Vitamin K, Aloe Vera
- Arnica: A homeopathic herb, arnica cream or gel is widely used to reduce bruising, swelling, and pain. Apply it gently to the affected area a few times a day.
- Vitamin K Cream: Vitamin K is crucial for blood clotting. Topical creams containing Vitamin K are believed to help reduce the appearance of bruises by assisting in the reabsorption of blood.
- Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing and healing properties, aloe vera gel can be applied to reduce inflammation and promote skin recovery.
- Natural Compresses: Witch Hazel, Apple Cider Vinegar
- Witch Hazel: This natural astringent can help tighten blood vessels and reduce swelling. Soak a cotton pad in witch hazel and apply it to the spot.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Diluted apple cider vinegar (one part ACV to two parts water) can be applied as a compress. It’s thought to improve circulation and aid in clearing the pooled blood.
- Dietary Aids: Pineapple (Bromelain), Berries (Flavonoids)
- Pineapple: Contains bromelain, an enzyme known for its anti-inflammatory properties, which can help break down proteins involved in bruising. Eating fresh pineapple or taking bromelain supplements might aid healing.
- Berries: Rich in flavonoids and Vitamin C, berries (like blueberries, strawberries) can strengthen capillary walls and reduce the likelihood of future bruising.
- Hydration and Healthy Diet: Maintaining good hydration and a diet rich in vitamins (especially C and K) and minerals supports overall skin health and capillary integrity, making it easier for your body to heal and potentially preventing future spots.
Over-the-Counter Solutions
For pain and inflammation associated with larger blood spots, over-the-counter medications can provide relief.
- Pain Relievers: Acetaminophen (Tylenol) can help manage pain. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) can reduce pain and swelling, but use them with caution if you are prone to bleeding or on blood thinners, as they can sometimes exacerbate bruising. Always consult your doctor if unsure.
- Topical Gels/Ointments: Some pharmacies offer specific topical gels designed to accelerate bruise healing, often containing ingredients like heparinoids or mucopolysaccharide polysulphate.
Medical Treatments and Dermatological Interventions
When home remedies aren’t enough, or if the blood spots are caused by an underlying condition, medical intervention becomes necessary.
- Addressing the Underlying Cause: This is the most critical step for blood spots caused by systemic issues. If a medication is the culprit, your doctor might adjust the dosage or switch to an alternative. For deficiencies, supplements will be prescribed. If an infection or autoimmune disease is identified, specific treatments for those conditions will be initiated. Treating the root cause is often the most effective way how to get rid of blood spots under skin permanently.
- Prescription Medications: Depending on the diagnosis, your doctor might prescribe medications. For certain types of vasculitis, corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be used. For severe bleeding disorders, specific clotting factor replacements might be necessary.
- Laser Therapy: For persistent, aesthetically bothersome blood spots or discoloration that remains after the blood has been reabsorbed (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation), dermatologists may use laser therapy. Lasers can target the pigment in the skin, helping to break down residual blood products and improve skin tone. This is usually considered for cosmetic improvement after the initial healing.
- Dermatological Procedures: In very rare cases, if a blood spot is large, painful, and accumulating significant blood (hematoma), a doctor might need to drain it. This is typically reserved for severe cases and not for common petechiae or purpura.
Proactive Steps: Preventing Future Blood Spots
Prevention is often the best medicine, especially when it comes to recurrent blood spots. Incorporating these proactive steps into your lifestyle can significantly reduce your chances of developing them.
Protect Your Skin: Wear Protective Gear
If you’re engaged in activities that carry a risk of injury (sports, gardening, DIY projects), wear appropriate protective gear like shin guards, long sleeves, or gloves to shield your skin from trauma.
Maintain a Nutrient-Rich Diet
Ensure your diet is abundant in vitamins and minerals, particularly:
- Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits, berries, bell peppers, and leafy greens, it strengthens capillary walls.
- Vitamin K: Present in leafy green vegetables (kale, spinach, broccoli), it’s essential for blood clotting.
- Bioflavonoids: Found in citrus fruits, berries, and dark chocolate, these compounds work with Vitamin C to strengthen blood vessels.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water keeps your skin healthy and supple, potentially making it more resilient to minor impacts.
Manage Medications Wisely
If you are on medications that increase your risk of bruising, discuss this with your doctor. Never stop or alter medication without professional medical advice, but your doctor might be able to suggest alternatives or strategies to minimize side effects.
Regular Health Check-ups
Routine medical check-ups can help identify and manage underlying conditions that might predispose you to blood spots, such as vitamin deficiencies, bleeding disorders, or liver issues, before they become more problematic.
Gentle Skin Care Practices
For those with thin or aging skin, be gentle. Avoid harsh scrubbing or vigorous rubbing, which can damage fragile capillaries. Moisturize regularly to keep skin supple and resilient.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Blood Spots Under Skin
How long do blood spots under the skin usually last?
Minor petechiae from straining might disappear within a few days. Bruises (ecchymosis) typically last 1-2 weeks, changing color as they heal. Larger purpura can take several weeks to fade. The duration largely depends on the size, cause, and individual healing capacity.
Can stress cause blood spots?
While stress doesn’t directly cause blood spots, severe emotional or physical stress can sometimes exacerbate underlying conditions or lead to behaviors (like rubbing or scratching) that might cause minor capillary damage. It’s more often an indirect factor.
Are blood spots always a sign of something serious?
No, most blood spots, especially small petechiae or common bruises, are harmless and resolve on their own. However, if they appear suddenly, are widespread, accompanied by other symptoms, or don’t fade, they can indicate a more serious underlying medical condition, warranting medical evaluation.
Is there a specific diet to prevent blood spots?
A diet rich in Vitamin C (citrus, berries, leafy greens) and Vitamin K (leafy greens) can help strengthen blood vessels and support proper clotting, potentially reducing the likelihood of easy bruising and blood spots. Bioflavonoids also contribute to capillary health.
When should I be worried about blood spots under my skin?
You should be worried and seek immediate medical attention if blood spots appear suddenly and are widespread, especially if accompanied by fever, severe headache, unexplained fatigue, easy bleeding How to remove black scars from skin unveiling your flawless radiance elsewhere, or signs of infection. If the spots don’t fade after several weeks or if you have a known bleeding disorder, consult your doctor.
Understanding how to get rid of blood spots under skin involves a holistic approach – from identifying their cause to applying appropriate remedies and taking preventive measures. While many spots are fleeting and benign, being informed allows you to distinguish between a minor skin quirk and a signal for professional medical advice. By empowering yourself with knowledge, you can approach these skin mysteries with confidence and work towards achieving clearer, healthier skin. Don’t hesitate to share this valuable information with friends and family, and always consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your skin’s health.