The appearance of clear bumps under skin can often be a source of confusion and frustration. One day your skin feels smooth and radiant, and the next, you notice these tiny, sometimes almost invisible, yet undeniably present, imperfections. While they might seem like a minor annoyance, these clear bumps under skin can impact your confidence and make you wonder about your skin’s health. But fret not! This comprehensive guide is here to illuminate the mysteries behind these common skin concerns, offering you insights into their causes, effective treatments, and proactive prevention strategies. Get ready to embark on a journey towards understanding your skin better and achieving that flawless, healthy glow you deserve!
Understanding the Diverse World of Clear Bumps Under Skin
Before we dive into specific conditions, it’s helpful to understand what we mean when we talk about clear bumps under skin. These aren’t typically red, inflamed pimples, nor are they usually deeply pigmented moles. Instead, they often manifest as small, raised areas that are either the same color as your skin or slightly whitish/pearly, and they feel like tiny grains or subtle elevations when you run your fingers across your skin.
What Exactly Are We Talking About?
Clear bumps under skin can vary significantly in size, texture, and location. They might be tiny, hard, and pearl-like, or soft, fluid-filled, and slightly larger. They can appear anywhere on the body – face, neck, chest, back, arms, or even around the eyes. Their common characteristic is their lack of significant redness or inflammation, at least initially, making them distinct from typical acne pustules or papules. Understanding this distinction is the first step in identifying the underlying cause.
Why Do They Appear?
The reasons behind the formation of clear bumps under skin are as varied as the bumps themselves. Generally, they arise from blockages within the skin’s intricate structures – our pores, hair follicles, and sebaceous (oil) glands. Sometimes, they’re a result of trapped skin cells, oil, or sweat. Other times, they can be a manifestation of viral infections or benign growths. Environmental factors, genetics, skincare habits, and even diet can play a role in their development. Pinpointing the exact cause is crucial for effective management and achieving smoother skin.
Common Culprits: Specific Conditions Causing Clear Bumps Under Skin
Let’s explore some of the most frequent conditions that present as clear bumps under skin. Each has its unique characteristics, causes, and recommended approaches.
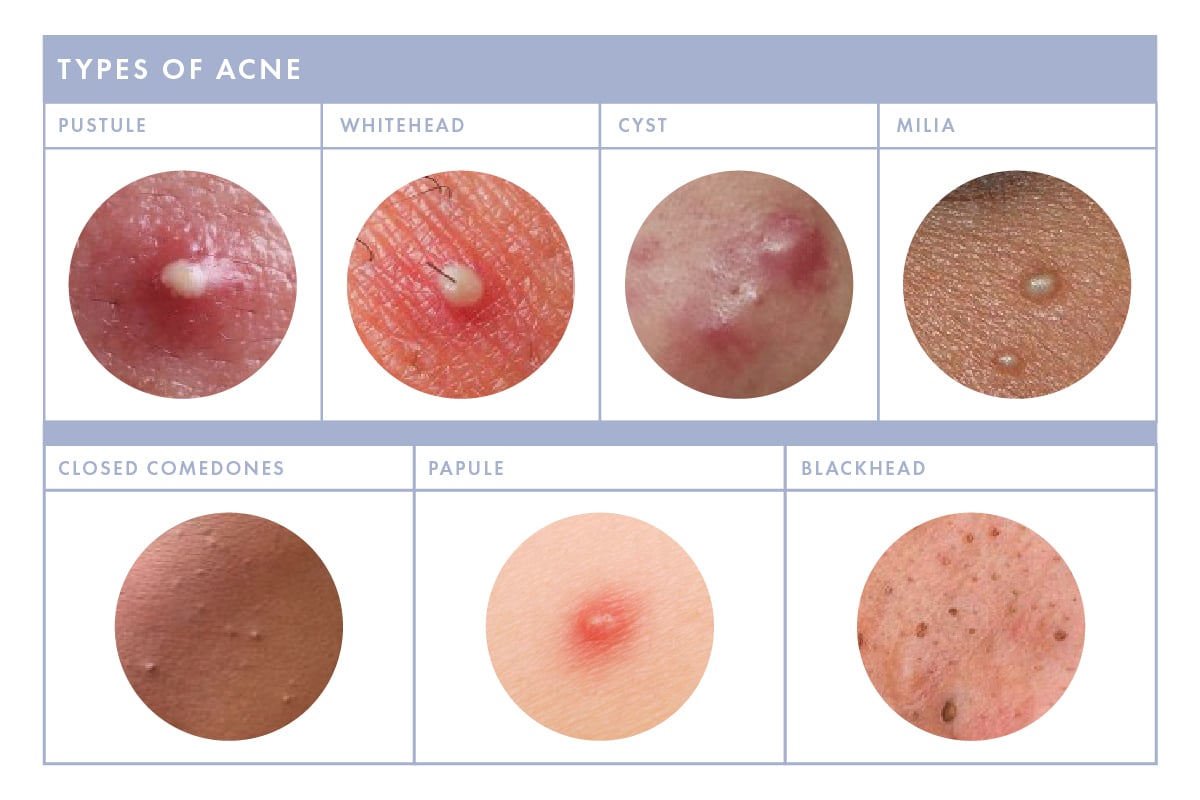
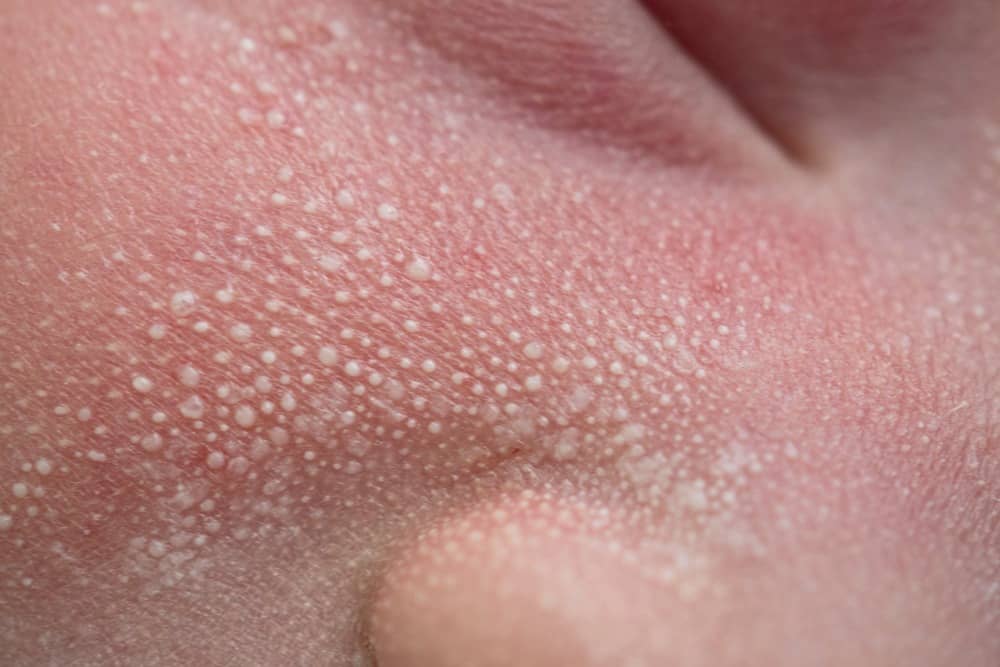
Milia: The Tiny, Pearly White Bumps
Milia are perhaps one of the most common forms of clear bumps under skin. These tiny, pearl-like cysts typically measure 1-2 millimeters and are often found around the eyes, nose, and cheeks, though they can appear anywhere. They form when dead skin cells become trapped beneath the skin’s surface, creating a small, hard, white or yellowish bump.
- Causes: Milia can be primary (occurring spontaneously) or secondary (developing after skin trauma, burns, sun damage, or certain skin conditions). They are common in newborns but can affect people of all ages. Heavy, occlusive skincare products can also contribute to their formation by trapping dead skin cells.
- Appearance: They are firm to the touch, non-inflamed, and don’t typically cause pain or itching.
- Treatment: Milia usually don’t resolve on their own in adults. A dermatologist can safely extract them using a sterile needle or lancet. Topical retinoids (like tretinoin or adapalene) can help encourage skin cell turnover and prevent new milia from forming.
- Prevention: Gentle exfoliation, avoiding heavy creams, and using sunscreen can help prevent milia.
Cysts: Deeper, Sometimes Fluid-Filled Lumps
While some cysts can be inflamed and red, many initially present as clear bumps under skin. These are typically larger and deeper than milia and can feel soft or firm.
- Epidermoid Cysts: These are common, benign cysts that develop when skin cells, instead of shedding, multiply and get trapped under the skin. They often have a central pore and can produce a cheesy, foul-smelling discharge if ruptured. They are usually skin-colored and feel firm.
- Sebaceous Cysts: Less common than epidermoid cysts, these arise from damaged or blocked sebaceous glands. They are filled with sebum (oil) and can also have a cheesy consistency.
- Appearance: Cysts are usually slow-growing, movable lumps under the skin. They can range from pea-sized to several centimeters.
- Treatment: Small, asymptomatic cysts may not require treatment. Larger, painful, or infected cysts often need surgical removal by a dermatologist. Incision and drainage might be performed for infected cysts, but complete removal of the cyst wall is necessary to prevent recurrence.
Folliculitis: Inflamed Hair Follicles
Folliculitis occurs when hair follicles become inflamed, often due to bacterial or fungal infection. While it can cause red, pus-filled bumps, it often starts as small, clear bumps under skin or tiny, itchy, skin-colored bumps, especially after shaving or wearing tight clothing.
- Causes: Shaving, waxing, tight clothing, excessive sweating, hot tubs, and certain medications can all contribute. Bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) and fungi (Malassezia yeast) are common culprits.
- Appearance: Small, itchy bumps that may have a central hair. They can appear on the scalp, neck, chest, back, buttocks, and legs.
- Treatment: Mild cases may clear up with good hygiene and antiseptic washes. Topical antibiotics or antifungals are often prescribed for persistent cases. Oral medications may be necessary for widespread or severe folliculitis.
- Prevention: Shave in the direction of hair growth, use a clean razor, avoid tight clothing, and shower after sweating.
Closed Comedones (Whiteheads): A Form of Acne
Closed comedones are a non-inflammatory type of acne that appear as small, skin-colored or whitish clear bumps under skin. They form when a hair follicle becomes completely blocked by a combination of oil (sebum) and dead skin cells, trapping the contents beneath the skin’s surface.
- Causes: Overproduction of sebum, abnormal shedding of skin cells, hormonal fluctuations, certain cosmetics, and genetics.
- Appearance: Small, slightly raised bumps without a visible opening, giving the skin a bumpy texture. They are most common on the face, especially the forehead and chin.
- Treatment: Topical retinoids (tretinoin, adapalene) are highly effective at promoting cell turnover and preventing blockages. Salicylic acid and alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) can also help exfoliate the skin.
- Prevention: A consistent skincare routine with gentle cleansing, exfoliation, and non-comedogenic products is key.
Sebaceous Hyperplasia: Enlarged Oil Glands
Sebaceous hyperplasia occurs when sebaceous glands become enlarged, often due to sun damage and aging. These are benign growths that present as small, yellowish or skin-colored clear bumps under skin, typically with a central indentation or "dimple."
- Causes: Primarily associated with sun exposure and aging, often appearing in middle-aged or older individuals.
- Appearance: Soft, dome-shaped bumps, usually on the forehead, cheeks, and nose. They are harmless but can be cosmetically bothersome.
- Treatment: Treatments include cryotherapy (freezing), electrocautery, laser therapy, or topical retinoids. These aim to reduce the size of the enlarged glands.
- Prevention: Sun protection is crucial in preventing their development.
Molluscum Contagiosum: A Viral Intruder
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that causes small, firm, dome-shaped clear bumps under skin with a characteristic central dimple (umbilication).
- Causes: Caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV), it spreads through direct skin-to-skin contact, contaminated objects, or sexual contact. It’s common in children and immunocompromised individuals.
- Appearance: Flesh-colored, pearly, or whitish bumps that can appear anywhere on the body, often in clusters. They are usually painless but can be itchy.
- Treatment: Often resolves on its own within months to years. Treatments include cryotherapy, curettage (scraping), laser therapy, or topical medications (e.g., cantharidin, imiquimod) to speed up resolution and prevent spread.
- Prevention: Avoid scratching, sharing towels, and direct contact with infected skin.
Syringomas: Benign Sweat Duct Tumors
Syringomas are harmless, non-cancerous tumors of the sweat ducts. They typically appear as small, flesh-colored or yellowish clear bumps under skin, often clustered around the eyes, on the eyelids, or on the chest and neck.
- Causes: The exact cause is unknown, but genetics may play a role. They are more common in women and tend to appear after puberty.
- Appearance: Small (1-3 mm), soft, slightly translucent bumps that are usually asymptomatic.
- Treatment: Syringomas are benign and do not require treatment. If cosmetically bothersome, they can be removed using electrocautery, laser therapy, or surgical excision, though recurrence is possible.
Pityrosporum Folliculitis (Fungal Acne): A Misunderstood Foe
Often mistaken for bacterial acne, Pityrosporum folliculitis is caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast (a type of fungus) in the hair follicles. It frequently presents as uniform, itchy clear bumps under skin, particularly on the chest, back, and shoulders, and sometimes on the face.
- Causes: Humidity, sweating, oily skin, certain antibiotics, and immunosuppression can trigger an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast.
- Appearance: Small, uniform, itchy papules and pustules, often without comedones (blackheads/whiteheads). It tends to worsen with sweat and heat.
- Treatment: Antifungal shampoos (containing ketoconazole or selenium sulfide) used as a body wash, or topical antifungal creams. Oral antifungals may be prescribed for more severe cases.
- Prevention: Showering immediately after sweating, using antifungal body washes, and wearing breathable fabrics.
When to Seek Professional Advice for Clear Bumps Under Skin
While many clear bumps under skin are harmless, it’s always wise to consult a healthcare professional, especially a dermatologist, if you’re unsure about the cause or if the bumps are bothering you.
Red Flags: What to Watch Out For
You should definitely seek professional advice if your clear bumps under skin:
- Are growing rapidly or changing in appearance.
- Become painful, itchy, red, or inflamed.
- Bleed or crust over.
- Are widespread or appear suddenly in large numbers.
- Are accompanied by other symptoms like fever or malaise.
- Don’t respond to over-the-counter treatments.
- Are causing you significant cosmetic concern or distress.
The Role of a Dermatologist
A dermatologist is a skin expert who can accurately diagnose the type of clear bumps under skin you have. They can differentiate between various conditions, rule out anything serious, and recommend the most effective treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Their expertise ensures you receive the right care, saving you time and potential frustration from self-diagnosing or trying ineffective remedies.
Navigating Treatment Options for Clear Bumps Under Skin
Once you have a diagnosis, a world of treatment options opens up. These can range from simple at-home care to advanced in-office procedures.
At-Home Care and Lifestyle Adjustments
For many types of clear bumps under skin, consistent at-home care can make a significant difference.
- Skincare Routine: Establish a gentle, consistent routine. Use a mild cleanser twice daily.
- Hygiene: Shower after sweating, especially if you’re prone to folliculitis or fungal acne.
- Diet: While not a direct cause for all bumps, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids can support overall skin health. Some individuals find that reducing dairy or high-glycemic foods helps with acne-related bumps.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated and support its natural barrier function.
- Avoid Picking: Resist the urge to pick, squeeze, or pop clear bumps under skin. This can lead to inflammation, infection, scarring, and spread of viral conditions.
Topical Treatments: Over-the-Counter and Prescription
Many clear bumps under skin respond well to topical applications.
- Exfoliants (AHAs, BHAs): Alpha Hydroxy Acids (like glycolic or lactic acid) and Beta Hydroxy Acids (like salicylic acid) help to exfoliate dead skin cells, preventing blockages. Salicylic acid is particularly good for closed comedones.
- Retinoids: Over-the-counter retinols or prescription retinoids (tretinoin, adapalene) are excellent for promoting cell turnover, clearing blocked pores, and preventing new bumps.
- Antifungals: For fungal folliculitis, topical creams or medicated shampoos containing ingredients like ketoconazole or selenium sulfide are effective.
- Antibiotics: For bacterial folliculitis or inflamed cysts, topical antibiotics may be prescribed.
In-Office Procedures
For stubborn or larger clear bumps under skin, a dermatologist How to clear up pimples on buttocks the ultimate guide to flawless skin can perform various in-office procedures.
- Extractions: For milia and closed comedones, a dermatologist can safely extract the contents using sterile tools.
- Chemical Peels: Medical-grade chemical peels can help exfoliate the skin more deeply, improving skin texture and reducing bumps.
- Laser Therapy: Lasers can be used to treat sebaceous hyperplasia, syringomas, and sometimes even milia or certain types of cysts.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing with liquid nitrogen can be used for sebaceous hyperplasia and molluscum contagiosum.
- Surgical Removal: Larger cysts or benign growths may require minor surgical excision for complete removal.
Proactive Steps: Preventing Clear Bumps Under Skin
Prevention is always better than cure! By adopting a few mindful habits, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing clear bumps under skin.
Establishing a Gentle Skincare Routine
- Cleanse Regularly: Wash your face twice daily with a mild, pH-balanced cleanser. Avoid harsh scrubbing, which can irritate the skin and exacerbate bumps.
- Exfoliate Thoughtfully: Incorporate a gentle chemical exfoliant (like a low-concentration AHA or BHA toner) 2-3 times a week to prevent dead skin cell buildup. Don’t over-exfoliate, as this can damage your skin barrier.
- Moisturize: Even oily skin needs moisture. Choose a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep your skin barrier healthy and balanced.
- Sun Protection: Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) is crucial. Sun damage can contribute to milia and sebaceous hyperplasia.
Smart Product Choices
- Non-Comedogenic: Always look for products labeled "non-comedogenic" or "non-acnegenic," meaning they are formulated not to clog pores.
- Avoid Heavy Oils: If you’re prone to bumps, be cautious with heavy facial oils or balms that can be occlusive and trap dead skin cells.
- Clean Makeup Brushes: Regularly clean your makeup brushes to prevent the transfer of bacteria and dead skin cells to your face.
Healthy Habits for Healthy Skin
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated helps your skin function optimally.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall skin health.
- Stress Management: Stress can impact hormonal balance and skin health, so finding ways to manage it is beneficial.
- Cleanliness: Change pillowcases regularly, especially if you have folliculitis or acne.
Conclusion
Discovering clear bumps under skin can certainly be a puzzle, but with the right knowledge and a proactive approach, achieving smooth, radiant skin is absolutely within reach! From the tiny milia to the more complex cysts and fungal folliculitis, understanding the specific cause is your first and most powerful step towards effective treatment and prevention. Remember, your skin is a dynamic organ, and it often communicates its needs through these subtle signs. Embrace a gentle yet consistent skincare routine, make informed lifestyle choices, and don’t hesitate to consult a dermatologist for personalized guidance. Your journey to a clearer, more confident complexion is a joyful one, filled with possibilities. Share your experiences and insights in the comments below – let’s build a community of healthy, happy skin enthusiasts!
FAQ Section
Q1: Are clear bumps under skin always serious?
A1: No, most clear bumps under skin are benign and not serious, such as milia, closed comedones, or sebaceous hyperplasia. However, some can indicate underlying conditions or become problematic if they grow, change, or become infected. It’s best to consult a dermatologist if you’re concerned.
Q2: Can diet cause clear bumps under skin?
A2: While diet isn’t the sole cause, certain dietary factors can influence skin health and potentially exacerbate conditions like acne (which includes closed comedones) or fungal folliculitis in some individuals. High-glycemic foods and dairy have been implicated by some studies, but individual responses vary. A balanced diet generally supports healthier skin.
Q3: How do I know if it’s milia or a whitehead?
A3: Milia are typically very small, firm, pearl-like, and appear under the skin without a visible pore opening. They are often found around the eyes. Whiteheads (closed comedones) are also small, skin-colored or whitish bumps, but they are a type of acne and can often be accompanied by other acne lesions. Milia are trapped skin cells, while whiteheads are trapped oil and skin cells in a pore.
Q4: Is it safe to pop clear bumps under skin?
A4: It is generally not recommended to pop clear bumps under skin yourself. Doing so can lead to inflammation, infection, scarring, and can even push the contents deeper, making the problem worse. For milia or closed comedones, professional extraction by a dermatologist is the safest and most effective method.
Q5: When should I see a doctor for clear bumps under skin?
A5: You should see a dermatologist if the bumps are persistent, growing, changing in color or shape, becoming painful, itchy, or inflamed, or if they are causing you significant cosmetic concern. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and lead to better outcomes.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-DermNetNZ-KeratosisPilaris-01-4f4d44d866e54ae692bce17f7a67c83f.jpg)